moslin preprint out
Mapping lineage-traced cells across time points with moslin
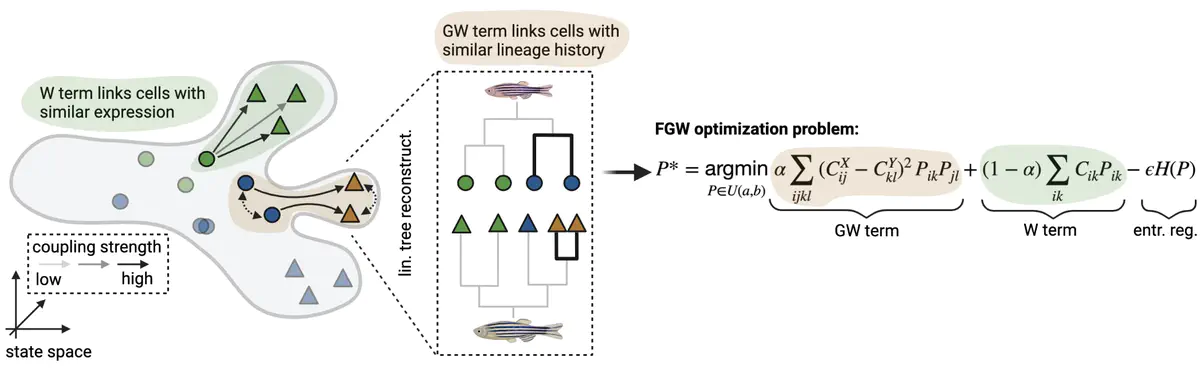
We’ve just released moslin, our new computational tool that maps single cells across time points based on lineage and gene expression information. To find out more, see the tweetorial or read the full preprint at bioRxiv. If you want to try moslin on your own lineage tracing data, check out the implementation at GibHub and the tutorial. Under the hood, moslin is based on moscot to solve the Fused Gromov-Wasserstein problem of relating both lineage and state across time. This project is a really fun collaboration with Zoe Piran from the Nitzan lab, Bastiaan Spanjaard from the Junker lab and Michal Klein, formerly Theislab, now Apple ML Research in Paris.
Abstract
Simultaneous profiling of single-cell gene expression and lineage history holds enormous potential for studying cellular decision-making beyond simpler pseudotime-based approaches. However, it is currently unclear how lineage and gene expression information across experimental time points can be combined in destructive experiments, which is particularly challenging for in-vivo systems. Here we present moslin, a Fused Gromov-Wasserstein-based model to couple matching cellular profiles across time points. In contrast to existing methods, moslin leverages both intra-individual lineage relations and inter-individual gene expression similarity. We demonstrate on simulated and real data that moslin outperforms state-of-the-art approaches that use either one or both data modalities, even when the lineage information is noisy. On C. elegans embryonic development, we show how moslin, combined with trajectory inference methods, predicts fate probabilities and putative decision driver genes. Finally, we use moslin to delineate lineage relationships among transiently activated fibroblast states during zebrafish heart regeneration. We anticipate moslin to play a crucial role in deciphering complex state change trajectories from lineage-traced single-cell data.